ATV-2 closing in
Europe’s ATV supply ship docks safely with Space Station
Eight days after launch, ESA’s latest Automated Transfer Vehicle, Johannes Kepler, completed a flawless rendezvous and docking with the International Space Station at 17:08 CET (16:08 GMT) to deliver essential supplies.
 © ESA
|
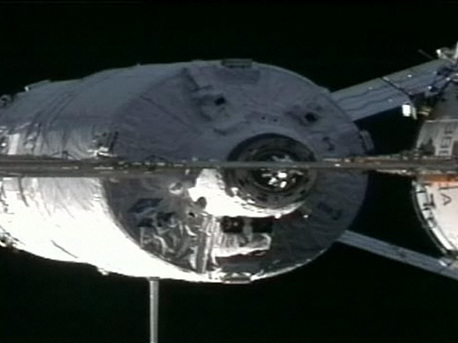
ATV Johannes Kepler in final moments before docking with ISS.
The approach and docking were achieved autonomously by its own computers, closely monitored by ESA and French space agency (CNES) teams at the ATV Control Centre in Toulouse, France, as well as the astronauts on the Station.
ATV's own second set of sensors and computers provided an independent check.
Although both ATV and the ISS orbit at 28 000 km/h, the relative speed during final approach remained below 7 cm/s and the accuracy within a few centimetres.
Johannes Kepler closed in on the ISS from behind in order to dock with Russia's Zvezda module.
At close range, the 20-tonne unmanned spaceship computed its position through sensors pointed at laser reflectors on the Station to determine its distance and orientation relative to its target.
ATV’s docking probe was captured by the docking cone inside Zvezda’s aft end at 16:59 CET (15:59 GMT). The closure of hooks completed the docking sequence some nine minutes later.
"With this smooth docking, Johannes Kepler proves to be a great example of the wave of innovation 'made in Europe'. We are more ready than ever to head into an era of autonomy in space exploration," said Simonetta di Pippo, ESA's Director for Human Spaceflight.
"Thanks to its flexibility, we can think of a wide variety of new space vehicles. ATV could evolve into a future reentry spacecraft to support future orbital infrastructures and exploration missions, carrying people and supplies to lunar orbit," added Mrs Pippo.
"This is very important for us and for all our partners in the ISS programme since, after the withdrawal of the Space Shuttle, ATV will be the largest servicing vehicle left to support the Station and it is our responsibility to deliver a proper service."
"What is happening up there is a lot more than the combination of space agencies, the engagement of ESA Member States and the dedication and 'savoir faire' of European Industry," said Jean-Jacques Dordain, ESA's Director General.
"We are contributing to the largest international cooperation ever conducted in the field of science and technology.
"We have a lot to learn here, not only through scientific research conducted onboard, but also with the ongoing space operations, in order to meet the challenges of tomorrow.
"The succession of vehicles recently launched to the ISS gives an idea of the level of joint operations the Station generates now that it is fully operational."
ATV Johannes Kepler was launched by an Ariane 5 from Europe's Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana, on 16 February. It will remain docked to the Station until June, serving as an additional module, providing a shirtsleeve environment for the astronauts and reboosts to move the complex to a higher altitude.
In the coming hours, the Station crew will open the hatch and enter ATV's pressurised cargo module to unload some 1760 kg of dry cargo, including food, clothes and equipment. They will also pump 860 kg of propellant and 100 kg of oxygen into Zvezda's tanks. ATV can carry about three times as much payload as Russia's Progress cargo ships. However, most of this load on Johannes Kepler is propellant for its own thrusters for periodic Station reboosts to compensate for atmospheric drag.
If required, ATV will also provide Station attitude control or even move the outpost out of the way of potentially dangerous space debris.
The docking of Johannes Kepler will be followed by NASA's docking of Space Shuttle Discovery, carrying the European-built Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module. With Europe's ATV and Leonardo, the US Shuttle, Japan's HTV-2 and two Russian Soyuz and one Progress docked simultaneously to the Station, the orbital outpost will set a new record for a manned space vehicle: it will provide more than 1000 cubic metres of pressurised volume and total more than 500 tonnes.
Source: ESA
ATV's own second set of sensors and computers provided an independent check.
Although both ATV and the ISS orbit at 28 000 km/h, the relative speed during final approach remained below 7 cm/s and the accuracy within a few centimetres.
Johannes Kepler closed in on the ISS from behind in order to dock with Russia's Zvezda module.
At close range, the 20-tonne unmanned spaceship computed its position through sensors pointed at laser reflectors on the Station to determine its distance and orientation relative to its target.
ATV’s docking probe was captured by the docking cone inside Zvezda’s aft end at 16:59 CET (15:59 GMT). The closure of hooks completed the docking sequence some nine minutes later.
"With this smooth docking, Johannes Kepler proves to be a great example of the wave of innovation 'made in Europe'. We are more ready than ever to head into an era of autonomy in space exploration," said Simonetta di Pippo, ESA's Director for Human Spaceflight.
"Thanks to its flexibility, we can think of a wide variety of new space vehicles. ATV could evolve into a future reentry spacecraft to support future orbital infrastructures and exploration missions, carrying people and supplies to lunar orbit," added Mrs Pippo.
"This is very important for us and for all our partners in the ISS programme since, after the withdrawal of the Space Shuttle, ATV will be the largest servicing vehicle left to support the Station and it is our responsibility to deliver a proper service."
"What is happening up there is a lot more than the combination of space agencies, the engagement of ESA Member States and the dedication and 'savoir faire' of European Industry," said Jean-Jacques Dordain, ESA's Director General.
"We are contributing to the largest international cooperation ever conducted in the field of science and technology.
"We have a lot to learn here, not only through scientific research conducted onboard, but also with the ongoing space operations, in order to meet the challenges of tomorrow.
"The succession of vehicles recently launched to the ISS gives an idea of the level of joint operations the Station generates now that it is fully operational."
ATV Johannes Kepler was launched by an Ariane 5 from Europe's Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana, on 16 February. It will remain docked to the Station until June, serving as an additional module, providing a shirtsleeve environment for the astronauts and reboosts to move the complex to a higher altitude.
In the coming hours, the Station crew will open the hatch and enter ATV's pressurised cargo module to unload some 1760 kg of dry cargo, including food, clothes and equipment. They will also pump 860 kg of propellant and 100 kg of oxygen into Zvezda's tanks. ATV can carry about three times as much payload as Russia's Progress cargo ships. However, most of this load on Johannes Kepler is propellant for its own thrusters for periodic Station reboosts to compensate for atmospheric drag.
If required, ATV will also provide Station attitude control or even move the outpost out of the way of potentially dangerous space debris.
The docking of Johannes Kepler will be followed by NASA's docking of Space Shuttle Discovery, carrying the European-built Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module. With Europe's ATV and Leonardo, the US Shuttle, Japan's HTV-2 and two Russian Soyuz and one Progress docked simultaneously to the Station, the orbital outpost will set a new record for a manned space vehicle: it will provide more than 1000 cubic metres of pressurised volume and total more than 500 tonnes.
Source: ESA
ATV-2 closing in
Europe’s ATV supply ship docks safely with Space Station
Eight days after launch, ESA’s latest Automated Transfer Vehicle, Johannes Kepler, completed a flawless rendezvous and docking with the International Space Station at 17:08 CET (16:08 GMT) to deliver essential supplies.
 © ESA
|
ATV Johannes Kepler in final moments before docking with ISS.
The approach and docking were achieved autonomously by its own computers, closely monitored by ESA and French space agency (CNES) teams at the ATV Control Centre in Toulouse, France, as well as the astronauts on the Station.
ATV's own second set of sensors and computers provided an independent check.
Although both ATV and the ISS orbit at 28 000 km/h, the relative speed during final approach remained below 7 cm/s and the accuracy within a few centimetres.
Johannes Kepler closed in on the ISS from behind in order to dock with Russia's Zvezda module.
At close range, the 20-tonne unmanned spaceship computed its position through sensors pointed at laser reflectors on the Station to determine its distance and orientation relative to its target.
ATV’s docking probe was captured by the docking cone inside Zvezda’s aft end at 16:59 CET (15:59 GMT). The closure of hooks completed the docking sequence some nine minutes later.
"With this smooth docking, Johannes Kepler proves to be a great example of the wave of innovation 'made in Europe'. We are more ready than ever to head into an era of autonomy in space exploration," said Simonetta di Pippo, ESA's Director for Human Spaceflight.
"Thanks to its flexibility, we can think of a wide variety of new space vehicles. ATV could evolve into a future reentry spacecraft to support future orbital infrastructures and exploration missions, carrying people and supplies to lunar orbit," added Mrs Pippo.
"This is very important for us and for all our partners in the ISS programme since, after the withdrawal of the Space Shuttle, ATV will be the largest servicing vehicle left to support the Station and it is our responsibility to deliver a proper service."
"What is happening up there is a lot more than the combination of space agencies, the engagement of ESA Member States and the dedication and 'savoir faire' of European Industry," said Jean-Jacques Dordain, ESA's Director General.
"We are contributing to the largest international cooperation ever conducted in the field of science and technology.
"We have a lot to learn here, not only through scientific research conducted onboard, but also with the ongoing space operations, in order to meet the challenges of tomorrow.
"The succession of vehicles recently launched to the ISS gives an idea of the level of joint operations the Station generates now that it is fully operational."
ATV Johannes Kepler was launched by an Ariane 5 from Europe's Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana, on 16 February. It will remain docked to the Station until June, serving as an additional module, providing a shirtsleeve environment for the astronauts and reboosts to move the complex to a higher altitude.
In the coming hours, the Station crew will open the hatch and enter ATV's pressurised cargo module to unload some 1760 kg of dry cargo, including food, clothes and equipment. They will also pump 860 kg of propellant and 100 kg of oxygen into Zvezda's tanks. ATV can carry about three times as much payload as Russia's Progress cargo ships. However, most of this load on Johannes Kepler is propellant for its own thrusters for periodic Station reboosts to compensate for atmospheric drag.
If required, ATV will also provide Station attitude control or even move the outpost out of the way of potentially dangerous space debris.
The docking of Johannes Kepler will be followed by NASA's docking of Space Shuttle Discovery, carrying the European-built Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module. With Europe's ATV and Leonardo, the US Shuttle, Japan's HTV-2 and two Russian Soyuz and one Progress docked simultaneously to the Station, the orbital outpost will set a new record for a manned space vehicle: it will provide more than 1000 cubic metres of pressurised volume and total more than 500 tonnes.
Source: ESA
ATV's own second set of sensors and computers provided an independent check.
Although both ATV and the ISS orbit at 28 000 km/h, the relative speed during final approach remained below 7 cm/s and the accuracy within a few centimetres.
Johannes Kepler closed in on the ISS from behind in order to dock with Russia's Zvezda module.
At close range, the 20-tonne unmanned spaceship computed its position through sensors pointed at laser reflectors on the Station to determine its distance and orientation relative to its target.
ATV’s docking probe was captured by the docking cone inside Zvezda’s aft end at 16:59 CET (15:59 GMT). The closure of hooks completed the docking sequence some nine minutes later.
"With this smooth docking, Johannes Kepler proves to be a great example of the wave of innovation 'made in Europe'. We are more ready than ever to head into an era of autonomy in space exploration," said Simonetta di Pippo, ESA's Director for Human Spaceflight.
"Thanks to its flexibility, we can think of a wide variety of new space vehicles. ATV could evolve into a future reentry spacecraft to support future orbital infrastructures and exploration missions, carrying people and supplies to lunar orbit," added Mrs Pippo.
"This is very important for us and for all our partners in the ISS programme since, after the withdrawal of the Space Shuttle, ATV will be the largest servicing vehicle left to support the Station and it is our responsibility to deliver a proper service."
"What is happening up there is a lot more than the combination of space agencies, the engagement of ESA Member States and the dedication and 'savoir faire' of European Industry," said Jean-Jacques Dordain, ESA's Director General.
"We are contributing to the largest international cooperation ever conducted in the field of science and technology.
"We have a lot to learn here, not only through scientific research conducted onboard, but also with the ongoing space operations, in order to meet the challenges of tomorrow.
"The succession of vehicles recently launched to the ISS gives an idea of the level of joint operations the Station generates now that it is fully operational."
ATV Johannes Kepler was launched by an Ariane 5 from Europe's Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana, on 16 February. It will remain docked to the Station until June, serving as an additional module, providing a shirtsleeve environment for the astronauts and reboosts to move the complex to a higher altitude.
In the coming hours, the Station crew will open the hatch and enter ATV's pressurised cargo module to unload some 1760 kg of dry cargo, including food, clothes and equipment. They will also pump 860 kg of propellant and 100 kg of oxygen into Zvezda's tanks. ATV can carry about three times as much payload as Russia's Progress cargo ships. However, most of this load on Johannes Kepler is propellant for its own thrusters for periodic Station reboosts to compensate for atmospheric drag.
If required, ATV will also provide Station attitude control or even move the outpost out of the way of potentially dangerous space debris.
The docking of Johannes Kepler will be followed by NASA's docking of Space Shuttle Discovery, carrying the European-built Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module. With Europe's ATV and Leonardo, the US Shuttle, Japan's HTV-2 and two Russian Soyuz and one Progress docked simultaneously to the Station, the orbital outpost will set a new record for a manned space vehicle: it will provide more than 1000 cubic metres of pressurised volume and total more than 500 tonnes.
Source: ESA