The future of the Milky Way
Whither goest thou, Milky Way?
As the young god Heracles forcefully suckled the breast of the Greek goddess Hera, she pushed him away and a spurt of her breast milk spilled across the sky. The name of our home galaxy, which does in fact appear in the night sky as a milky band, originates from this Greek legend. The term 'galaxy' stems from the ancient Greek word for milk, 'gala'.
 © James Gitlin
|
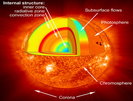
This artist's impression shows the collision between the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy, many billions of years in the future. This scenario is based on observed data and analytically grounded fantasy.
After the well-known Andromeda Nebula (more accurately, the Andromeda Galaxy), the Milky Way is the second-largest galaxy in a group of over 50 galaxies that is known as the 'Local Group'. The Milky Way and Andromeda Galaxy are moving towards each other at a speed of 80 miles per second. In around three billion years, the two galaxies could collide. It is not yet possible to forecast exactly what will happen but, using observed data and a little imagination, a probable future scenario can be developed. The critical factor is whether the two galaxies are moving straight towards each other – then they will collide head-on – or whether they are approaching each other on a circular path – then the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy could narrowly miss one another.
Worlds colliding
Observations of other pairs of galaxies that converge indicate that the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy would also first 'dance around' each other in a spiral and then melt together to form a large elliptical galaxy. Nothing will happen to the stars themselves in the process, as they are light years away from each other. However, according to model calculations, their orbit around the center of the newly formed galaxy could change – from a circular orbit to an elliptical one. Gas atoms and dust from the two galaxies inevitably collide with each other and thus change their speed in relation to the stars – the new elliptical galaxy starts to lack interstellar matter from which new stars are formed.
Human beings will most probably not live to see these events (see question 'How long will the Sun continue to shine?') – if they do, however, then there is already a name for their new home galaxy: Milkomeda (from Milky Way and Andromeda).
German Aerospace Center
Worlds colliding
Observations of other pairs of galaxies that converge indicate that the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy would also first 'dance around' each other in a spiral and then melt together to form a large elliptical galaxy. Nothing will happen to the stars themselves in the process, as they are light years away from each other. However, according to model calculations, their orbit around the center of the newly formed galaxy could change – from a circular orbit to an elliptical one. Gas atoms and dust from the two galaxies inevitably collide with each other and thus change their speed in relation to the stars – the new elliptical galaxy starts to lack interstellar matter from which new stars are formed.
Human beings will most probably not live to see these events (see question 'How long will the Sun continue to shine?') – if they do, however, then there is already a name for their new home galaxy: Milkomeda (from Milky Way and Andromeda).
German Aerospace Center
The future of the Milky Way
Whither goest thou, Milky Way?
As the young god Heracles forcefully suckled the breast of the Greek goddess Hera, she pushed him away and a spurt of her breast milk spilled across the sky. The name of our home galaxy, which does in fact appear in the night sky as a milky band, originates from this Greek legend. The term 'galaxy' stems from the ancient Greek word for milk, 'gala'.
 © James Gitlin
|
This artist's impression shows the collision between the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy, many billions of years in the future. This scenario is based on observed data and analytically grounded fantasy.
After the well-known Andromeda Nebula (more accurately, the Andromeda Galaxy), the Milky Way is the second-largest galaxy in a group of over 50 galaxies that is known as the 'Local Group'. The Milky Way and Andromeda Galaxy are moving towards each other at a speed of 80 miles per second. In around three billion years, the two galaxies could collide. It is not yet possible to forecast exactly what will happen but, using observed data and a little imagination, a probable future scenario can be developed. The critical factor is whether the two galaxies are moving straight towards each other – then they will collide head-on – or whether they are approaching each other on a circular path – then the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy could narrowly miss one another.
Worlds colliding
Observations of other pairs of galaxies that converge indicate that the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy would also first 'dance around' each other in a spiral and then melt together to form a large elliptical galaxy. Nothing will happen to the stars themselves in the process, as they are light years away from each other. However, according to model calculations, their orbit around the center of the newly formed galaxy could change – from a circular orbit to an elliptical one. Gas atoms and dust from the two galaxies inevitably collide with each other and thus change their speed in relation to the stars – the new elliptical galaxy starts to lack interstellar matter from which new stars are formed.
Human beings will most probably not live to see these events (see question 'How long will the Sun continue to shine?') – if they do, however, then there is already a name for their new home galaxy: Milkomeda (from Milky Way and Andromeda).
German Aerospace Center
Worlds colliding
Observations of other pairs of galaxies that converge indicate that the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy would also first 'dance around' each other in a spiral and then melt together to form a large elliptical galaxy. Nothing will happen to the stars themselves in the process, as they are light years away from each other. However, according to model calculations, their orbit around the center of the newly formed galaxy could change – from a circular orbit to an elliptical one. Gas atoms and dust from the two galaxies inevitably collide with each other and thus change their speed in relation to the stars – the new elliptical galaxy starts to lack interstellar matter from which new stars are formed.
Human beings will most probably not live to see these events (see question 'How long will the Sun continue to shine?') – if they do, however, then there is already a name for their new home galaxy: Milkomeda (from Milky Way and Andromeda).
German Aerospace Center